Tooth resorption is a dental condition characterized by the gradual breakdown of tooth structure. If not addressed, it can result in pain and infection and potentially lead to tooth loss. Understanding tooth resorption is crucial for both dental professionals and patients, as early detection and intervention can significantly improve outcomes. This post will provide a detailed overview of tooth resorption, its types, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for effective results
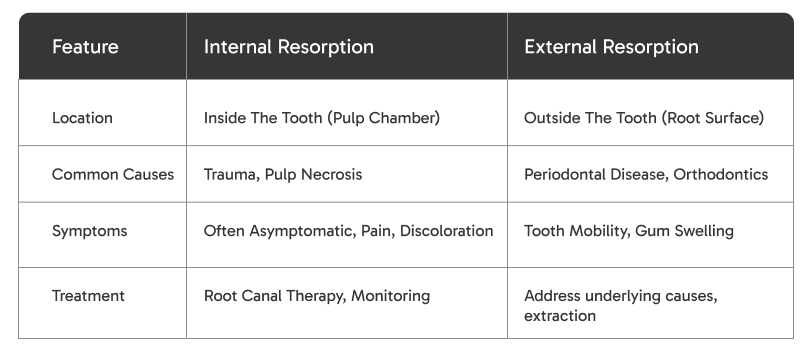
Tooth resorption occurs when the body’s natural processes break down the hard tissues of the teeth. It can be classified into two main types: internal resorption and external resorption. Understanding these types is vital for recognizing symptoms and seeking appropriate treatment.
Understanding tooth resorption is essential for:
Definition: Internal resorption occurs within the tooth, specifically affecting the pulp chamber. This type often goes unnoticed until it reaches an advanced stage.
Causes:
Symptoms:
Definition: External resorption affects the outer surface of the tooth, particularly the roots. It is more commonly associated with dental procedures or periodontal disease.
Causes:
Symptoms:
Tooth resorption can result from several factors, including:
Diagnosis usually involves:
Treatment varies based on the type and severity of resorption:
To reduce the risk of tooth resorption, consider the following:
Tooth resorption is a condition that requires attention to maintain oral health. By understanding its types, causes, symptoms, and treatment options, you can take proactive steps to safeguard your dental health. If you suspect tooth resorption or have concerns about your teeth, consult with your dentist promptly for evaluation and guidance.
Tooth resorption is a dental condition in which the body breaks down the hard tissues of a tooth, which, if untreated, can lead to potential pain, infection, and tooth loss.
Trauma, infections, periodontal disease, hormonal changes, or excessive pressure from orthodontic treatment can cause tooth resorption.
There are two main types: internal resorption, which occurs within the tooth structure, and external resorption, which affects the outer surface of the tooth.
Internal resorption is often caused by trauma to the tooth, chronic inflammation, or pulp necrosis.
External resorption is commonly linked to periodontal disease, orthodontic treatment, or trauma to the tooth.
Symptoms can include tooth pain, discoloration, swelling, tooth mobility, and sensitivity to pressure and temperature.
Diagnosis typically involves dental X-rays, clinical examinations, and pulp vitality testing to assess tooth health.
Treatment options vary by type: internal resorption may be treated with root canal therapy, while external resorption may require addressing the underlying causes or extraction in severe cases.
Preventative measures include maintaining good oral hygiene, regular dental check-ups, and using protective gear during contact sports.